Classification of disease type for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
Autoimmune alveolar proteinosis accounts for 92%
― Classification of disease type for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
― Classification of disease type for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
Alveolar proteinosis is diagnosed by pathological examination (examination of cells through bronchoalveolar lavage using broncho-fiberscopy, and biopsy of lung tissue using forceps).
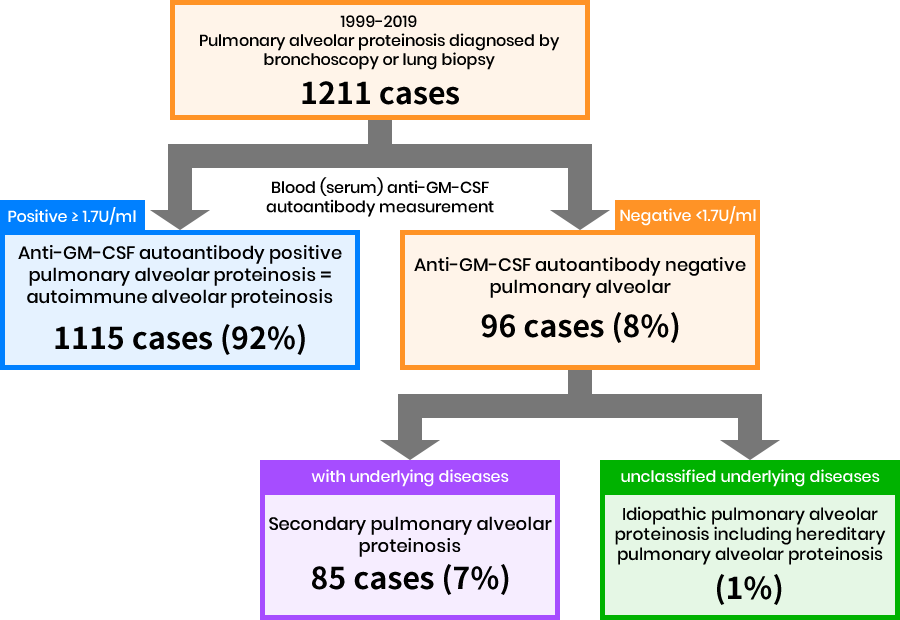
- A positive serum anti-GM-CSF autoantibody measurement (1.7 U/ml or more) indicates autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis.
- Of those testing negative for anti-GM-CSF autoantibodies in the serum, if there is an obvious underlying disease that causes pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, such as hematological disorder, infectious disease, or collagen disease, doctors suspect secondary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis.
- When the underlying disease causing the disease is unknown, the doctors have to classify the disease as idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, but after further intensive and extensive examination, some cases may be classified as hereditary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis.
- The proportions diagnosed as autoimmune alveolar proteinosis, secondary alveolar proteinosis, and idiopathic alveolar proteinosis are 92%, 7%, and 1%, respectively.