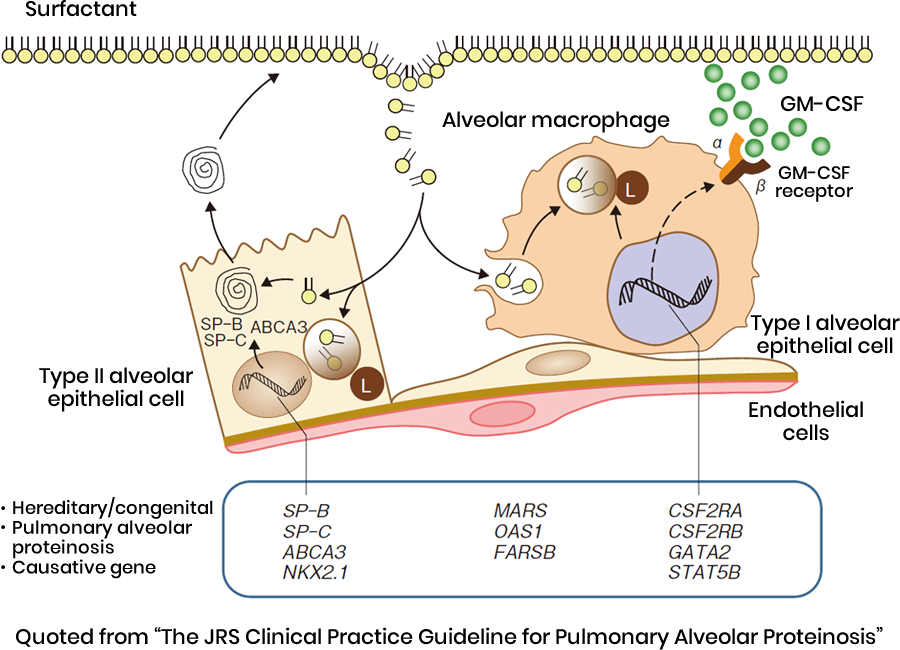
Genes responsible for hereditary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
Currently known causes include abnormalities in the GM-CSF receptor genes (CSF2RA, CSF2RB) and the hematopoietic transcription factors GATA2 and STAT5B genes, which are genetic abnormalities in alveolar macrophages. In addition, surfactant-related gene abnormalities include SFTPB (SP- B), SFTPC (SP-C), and ABCA3. Other abnormalities in the NKX2.1 (TTF1) gene, which is important for the morphogenesis of the lungs, brain, and thyroid, may also be the cause.
In addition, hereditary/congenital alveolar proteinosis caused by mutations in genes, such as MARS, OAS1, and FARSB, has been reported. It is important to note that mutations in the same gene may exhibit different clinical symptoms (onset in childhood or adulthood; histopathology other than alveolar proteinosis).